Deploy on Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud
Follow the instructions in this guide to setup DronaHQ in self hosted environment on Amazon elastic computing cloud (EC2).
Prerequisite
To deploy DronaHQ on Amazon EC2, you should have:
DronaHQ License Key, which you can get from DronaHQ Self Hosted Portal.- Basic understanding of
AWSandAmazon EC2. - Working AWS account with permissions to manage EC2.
Following are some references, which can help you sail through AWS EC2.
- Best practices to protect your account's root user
- Tutorial: Get started with Amazon EC2 Linux instances
- Granting required permissions for Amazon EC2 resources
- Best practices for Amazon EC2
- Amazon EC2 service quotas
- Connect to your Linux instance from Linux or macOS using SSH
1. Create EC2 instance
On AWS EC2 dashboard, Click Launch Instance.
Name your instance, to identify it later.
Optionally you can add some Tags (e.g.
app = dronahq). This makes it easier to find if you have a lot of instances.Select
UbuntuAMI with ubuntu version20.04or higher and64-bit (x84)architecture.Select an instance type of your choice with minimum configuration as
t3.medium.Create or Select
SSH key pair, This will be needed to connect to the instance via SSH.Ensure you select the same
VPCthat also includes the databases & API’s that you want to connect.You can create new
Security Groupor choose existing one. Modify inbound rules and add ports80,443,22and8080, with sources set to0.0.0.0/0and::/0.You can set sources as your internal network address which will make it available only on your internal network.
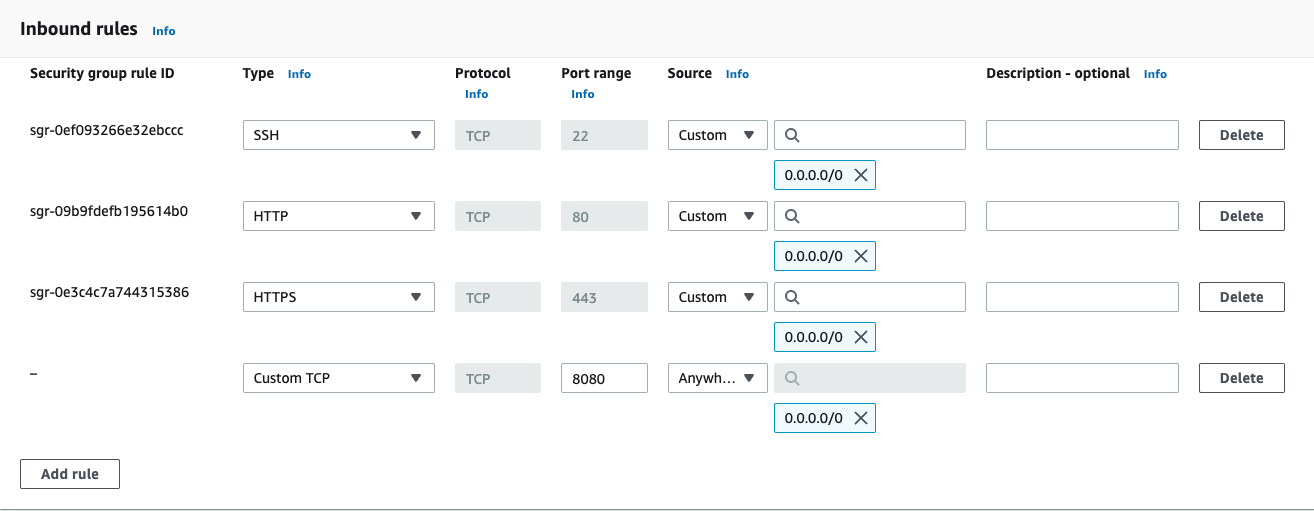
We need to open ports
80(http) and443(https) so you can connect to the server from a browser, as well as port22(ssh) so that you can ssh into the instance to configure it and run DronaHQ. By default on a vanilla EC2, DronaHQ will run on port8080.Configure the storage volume to have at least
60 GiBof general purpose SSD.In the Summary section, click on Launch Instance to start your instance.
2. Connect to your Linux instance using an SSH client
Use the following procedure to connect to your Linux instance using an SSH client. If you receive an error while attempting to connect to your instance, see Troubleshoot connecting to your instance.
Connect to your instance using SSH
In a terminal window, use the ssh command to connect to the instance. You specify the path and file name of the private key (.pem), the user name for your instance, and the public DNS name or IPv6 address for your instance. For more information about how to find the private key, the user name for your instance, and the DNS name or IPv6 address for an instance, see Locate the private key and set permissions and Get information about your instance. To connect to your instance, use one of the following commands.
- (Public DNS) To connect using your instance's public DNS name, enter the following command.
ssh -i /path/key-pair-name.pem instance-user-name@instance-public-dns-name - (IPv6) Alternatively, if your instance has an IPv6 address, to connect using your instance's IPv6 address, enter the following command.
ssh -i /path/key-pair-name.pem instance-user-name@instance-IPv6-address
You see a response like the following:
The authenticity of host 'ec2-198-51-100-1.compute-1.amazonaws.com (198-51-100-1)' can't be established.
ECDSA key fingerprint is l4UB/neBad9tvkgJf1QZWxheQmR59WgrgzEimCG6kZY.
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)?- (Public DNS) To connect using your instance's public DNS name, enter the following command.
(Optional) Verify that the fingerprint in the security alert matches the fingerprint that you previously obtained in (Optional) Get the instance fingerprint. If these fingerprints don't match, someone might be attempting a man-in-the-middle attack. If they match, continue to the next step.
Enter
yes.You see a response like the following:
Warning: Permanently added 'ec2-198-51-100-1.compute-1.amazonaws.com' (ECDSA) to the list of known hosts.
3. Download DronaHQ Self Hosted
There are two ways, you can download DronaHQ Self Hosted.
a. Cloning Git repository
To clone from git repository, run following command.
git clone https://github.com/dronahq/self-hosted.git dronahq-self-hosted
Above command will create new folder in your present working directory with name dronahq-self-hosted.
b. Download and extract compressed package from DronaHQ
To download compressed package from DronaHQ, run following command
curl -L -fsSL -o ./master.zip "https://license.dronahq.com/self-hosted/master.zip" && unzip master.zip && mv master dronahq-self-hosted
4. Change working directory
We have to change working directory to dronahq-self-hosted for playing with DronaHQ.
Use following command.
cd dronahq-self-hosted
5. Setup Externalize databases
For deployment on AWS EC2, it is mandatory to setup external databases for both MYSQL and MONGODB.
Please follow our guide on Configure external databases.
6. Setup DronaHQ Environment
Running this script will clear your existing installation if you have any. It will setup completely new environment. It will create back of your current environment and storage directory with time stamp followed by file/folder name.
To setup dronahq environment, you have to run ./dronahq_setup already present in your working directory.
./dronahq_setup
7. Update environment variables
DronaHQ writes all configurable environment variables in file dronahq.env. Please make sure you have all mandatory variables are in place.
i. LICENSE_KEY
LICENSE_KEY is one of the mandatory and essential environment variable. please verify that you have it in dronahq.env.
If not you can add this variable. Following is the example of how this variable should look like in environment file.
LICENSE_KEY=< DRONAHQ-LICENSE-KEY >
If you don't have DronaHQ license key for self hosted, you can sign up for DronaHQ self hosted and get your license key by logging in to self-hosted portal.
ii. BUILDER_URL
This variable specifies how do yo want to access DronaHQ.
- Protocol [ http/ https]
- Access domain [ Localhost/ IP address/ Domain Name]
Example 1. If you are using DronaHQ on local machine.
BULDER_URL=http://localhost
Example 2. If you have configured DronaHQ on server and want to use it with server's public IP address.
# replace your ip address here
BUILDER_URL=http://198.51.100.1
Example 3. If you have mapped your domain name to server's IP address.
# replace your domain name
BUILDER_URL=http://dronahq.example.com
iii. Database configuration variables
Configure variables for external MYSQL credentials
MYSQL_HOST, MYSQL_USER, MYSQL_PASSWORD, MYSQL_PORT
MYSQL_HOST=mysql.example.com
MYSQL_USER=dronahq
MYSQL_PASSWORD=secret-password
MYSQL_PORT=3306
Configure variables for external MONGODB credentials
MONGODB_HOST, MONGODB_USER, MONGODB_PASSWORD, MONGODB_PORT
MONGODB_HOST=mongodb.example.com
MONGODB_USER=dronahq
MONGODB_PASSWORD=secret-password
MONGODB_PORT=27017
iv. Other environment variables
You can also checkout other Environment Variables, which can enable advance options for you to use DronaHQ Self Hosted.
8. Restart DronaHQ
You can apply all new changes in configuration, and restart DronaHQ simply by running following command.
sudo docker compose up -d
9. Verify that containers are running
You can use following command to check running docker containers.
sudo docker compose ps
It should look something like this
