Snowflake
Snowflake is a cloud-based data warehousing platform that offers fast and flexible analytics. It enables seamless handling of large-scale data while providing advanced data sharing and processing capabilities.
Prerequisite
Authentication Requirements: To establish a connection with your Snowflake instance, you will require specific authentication credentials. You have the choice of either of the following two credential options:
- Snowflake database username and password.
- Alternative authentication methods (excluding AWS IAM authentication).
Connection Details:
- Hostname of the Snowflake database.
- Port number for database communication.
- The designated database name within the Snowflake host.
Firewall Rules:
- Set up your firewall settings to permit DronaHQ's IP whitelist for access to your Snowflake host.
Having these essential prerequisites in place will ensure a seamless integration of Snowflake with DronaHQ, facilitating efficient data management and utilization.
Configuring Connector in DronaHQ
Configure your database category using the provided details. Validate connection with Test connection and Save
settings for secure database setup.
DronaHQ can Auto fill crucial connection values like host, name, password, and more from the connector's connection string.
Whitelisting DronaHQ
To begin the process, you must first whitelist DronaHQ. Follow these steps meticulously:
Set Admin Privileges for User Role: Initiate the procedure by granting yourself administrative privileges by assuming the role of "securityadmin." Employ the following command within the worksheets:
USE ROLE securityadmin;Create Network Policy and Whitelist IPs: Proceed to create a network policy to facilitate whitelisting of IPs. Implement the ensuing command to achieve this:
CREATE NETWORK POLICY DHQ_WHITELIST ALLOWED_IP_LIST = ('Your IP', 'DronaHQ IP', ...);Apply Network Policy: Execute the subsequent command to apply the newly created network policy:
ALTER ACCOUNT SET NETWORK_POLICY = DHQ_WHITELIST;Verify Policy Configuration: Confirm the network policy configuration and details by querying it using the following command:
DESC NETWORK POLICY DHQ_WHITELIST;Account Name Retrieval: To ensure accurate account whitelisting, extract the account name from your Snowflake database URL. Access the URL at
https://<account-name>.snowflakecomputing.com.- For instance, if your URL is
https://dronahq-test-account.snowflakecomputing.com, the account name would bedronahq-test-account. - In AWS scenarios, URLs might resemble
https://dronahq-test-account.us-east-2.aws.snowflakecomputing.com, where the account name isdronahq-test-account.us-east-2.aws. - In the case of Azure, URLs could appear as
https://dronahq-test-account.west-us-2.azure.snowflakecomputing.com, and the corresponding account name would bedronahq-test-account.west-us-2.azure.
- For instance, if your URL is
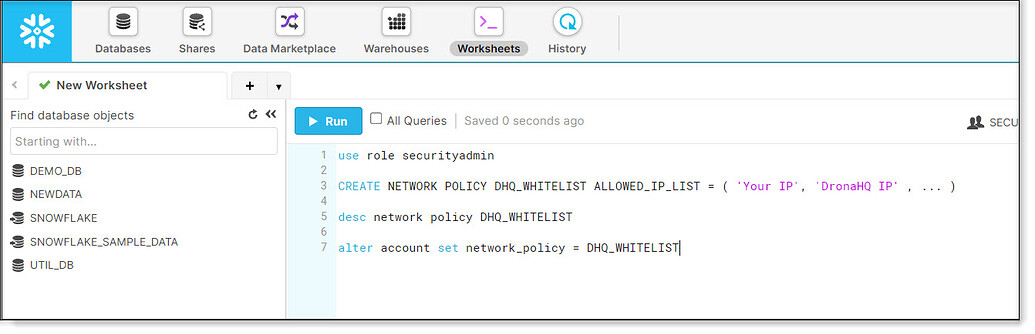
General
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Account Identifier | Provide the account identifier which uniquely identifies a Snowflake account within your organization, as well as throughout the global network |
| Account Name | Enter the Snowflake Account name |
| Database Name | Enter the Database name |
| Database Schema | Enter the Schema name |
| Authentication | Select authentication methods between Password based and Key pair. |
| Username | Enter the Username |
| Password | Enter the Password |
| Data Warehouse | Enter the Data Warehouse name |
| User Role | Enter the User Role |
| Private Key | Enter the private encrypted key. |
Admin
| Advanced Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Connection Options | The key and value connection options in database configuration refer to specific settings (keys) and their corresponding values that dictate how the application connects to the database |
| Whitelist IP | Enhance security by restricting database access to specific whitelisted IP addresses. |
Adding Database Queries
After configuring the connector, access it in your Connector Library.
Click Add query once the connection is established. Create queries, run them, and view responses.
Use double curly brackets for dynamic variables. Test with sample values before saving. Link dynamic variables to controls/actions for runtime use.
Saved queries appear under your connector in Connector Library.
Supported Query Operations
| Operations | Description |
|---|---|
| Raw SQL Query | Execute various SQL operations directly, e.g., SELECT * FROM TableName; |
| Stored Procedure Call | Call stored procedures, e.g., EXEC usp_GetInfo; to perform specific tasks or retrieve data from the database. |
Using Snowflake Connector
Data Bind using Data Query
Read/Display Data Query for Snowflake:
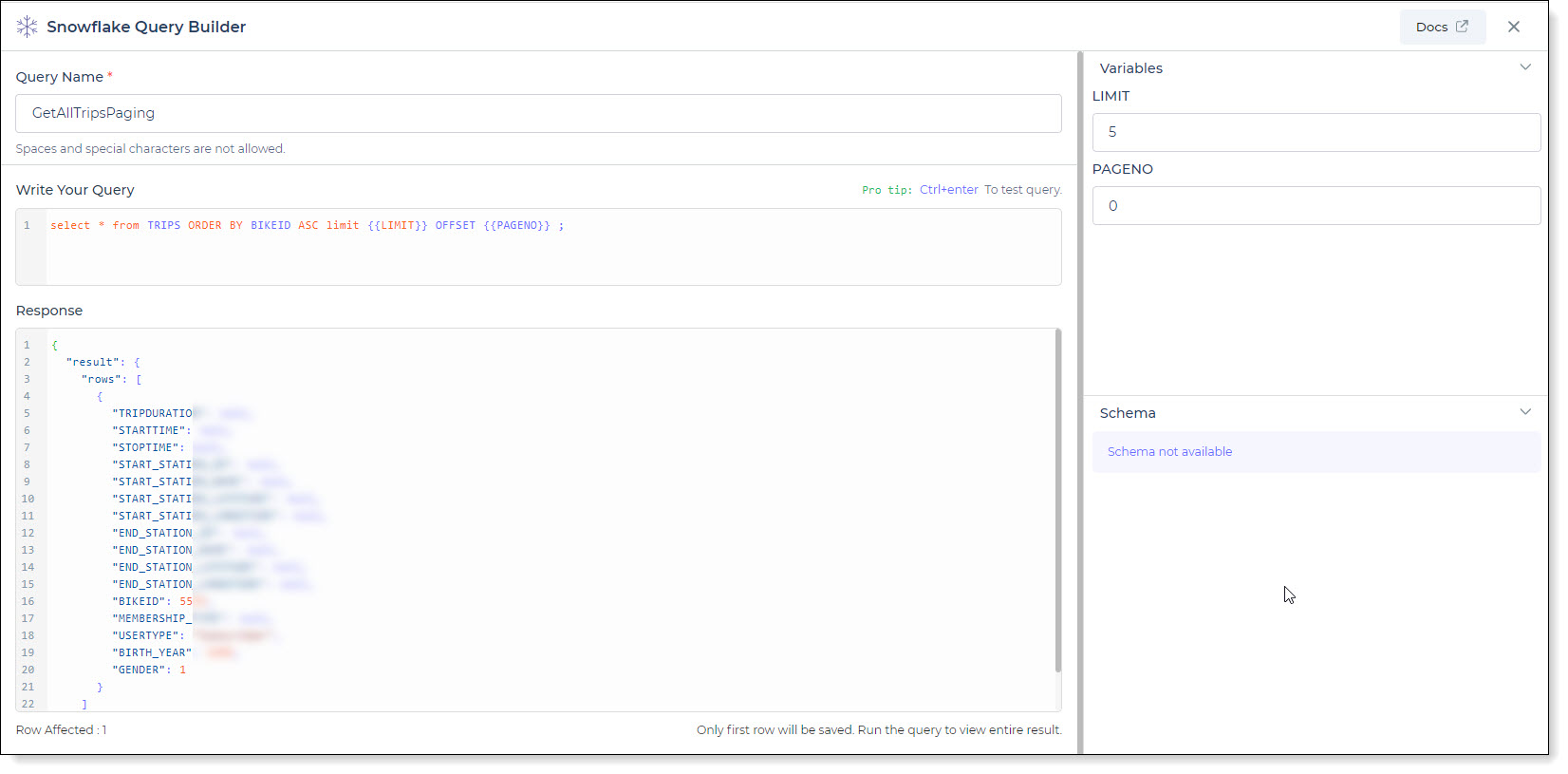
Begin by crafting an SQL query to extract data from your Snowflake database. For example, let's consider a scenario
where you want to retrieve data from the TRIPS table with ordering, limiting, and offset. The SQL query is:
Query used:
SELECT * FROM TRIPS ORDER BY BIKEID LIMIT {{limit}} OFFSET {{offset}};
Query explanation:
This SQL query retrieves all rows and columns from the TRIPS table and orders them by BIKEID. The results are
limited based on the {{limit}} value and offset by the {{offset}} value, which are dynamic variables.
Integrate the fetched data into your application's interface.
a. Access the Controls section and introduce the Table grid control.
b. Navigate to Data Bind Options -> Quick Select -> Database Queries.
c. Opt for the Snowflake connector and choose the query that aligns with your data presentation goals.
By following these steps, you can seamlessly retrieve and display data from the TRIPS table using the Snowflake
Connector, enhancing your application's functionality and user experience with ordering, limiting, and offset features.