Query Builder
The Query Builder control empowers you to create custom queries for situations requiring server-side filtering, utilizing criteria defined during runtime. By integrating it with your connectors, you can dynamically select and apply queries to your data sources. This advantageously enables dynamic filtering for controls like Table Grid and List controls, ensuring efficient data retrieval based on specific criteria.
Define Schema
You can define your Query Builder schema either statically using Properties section or dynamically using Bind Data -> Schema option. Schema binding allows you to specify the structure of your query that can be build using Query Builder control keeping data type of the data as defined in schema. This allows Query Builder to provide options in rules according to data defined in Schema.
Here's how you can use schema binding:
Use JSON notation to define the structure of your data. Include key-value pairs to represent each field along with its data type. For example:
{
[
{
"label": "Status",
"value": "status",
"enum": [
{
"label":"Approved",
"value":"approved"
},
{
"label":"Rejected",
"value":"rejected"
},
{
"label":"Pending",
"value":"pending"
}
]
},
{
"label": "User Name",
"value": "username",
"type": "text"
},
{
"label": "Email",
"value": "email",
"type": "text"
},
{
"label":"Age",
"value":"age",
"type":"number"
}
]
}
You can alternatively use the Bind Data Section to bind the schema to the control with above format. This allows the control to fetch data dynamically from data queries, sheets, or custom functions and display it according to the specified schema.
Binding Data Options
The Query Builder control provides either of the two methods to initialize a query from the start:
Additionally, you can define the schema structure during initialization using:
RAW_JSON
Provide a RAW JSON in below format to initialize the Query Control with preset rules and orderBy clauses. This allows for precise control over the query structure, enabling you to define complex filter conditions in detail right at the initialization of the control.
Sample RAW JSON:
{
"id": "g-RQpZdXIWdZhAmFoJO",
"rules": [],
"orderBy": [
{
"id": "o-RvsitaQBPeStckGkC",
"field": "username",
"direction": "asc"
}
],
"combinator": "AND"
}
However, you can also dynamically fetch this data using Bind options by retrieving information from Data queries, Sheets, or Custom functions and binding the response to the Data Bind option.
Query
You can also, alternatively provide Query option instead of RAW JSON to initialize the Query Control with preset rules and orderBy clauses. It provides a more user-friendly approach to initialize query control. This simplifies the overall process to directly provide query to the control when it gets start. So whatever query the user put in the data bind section, it will reflect in the control as pre-provided conditions/query.
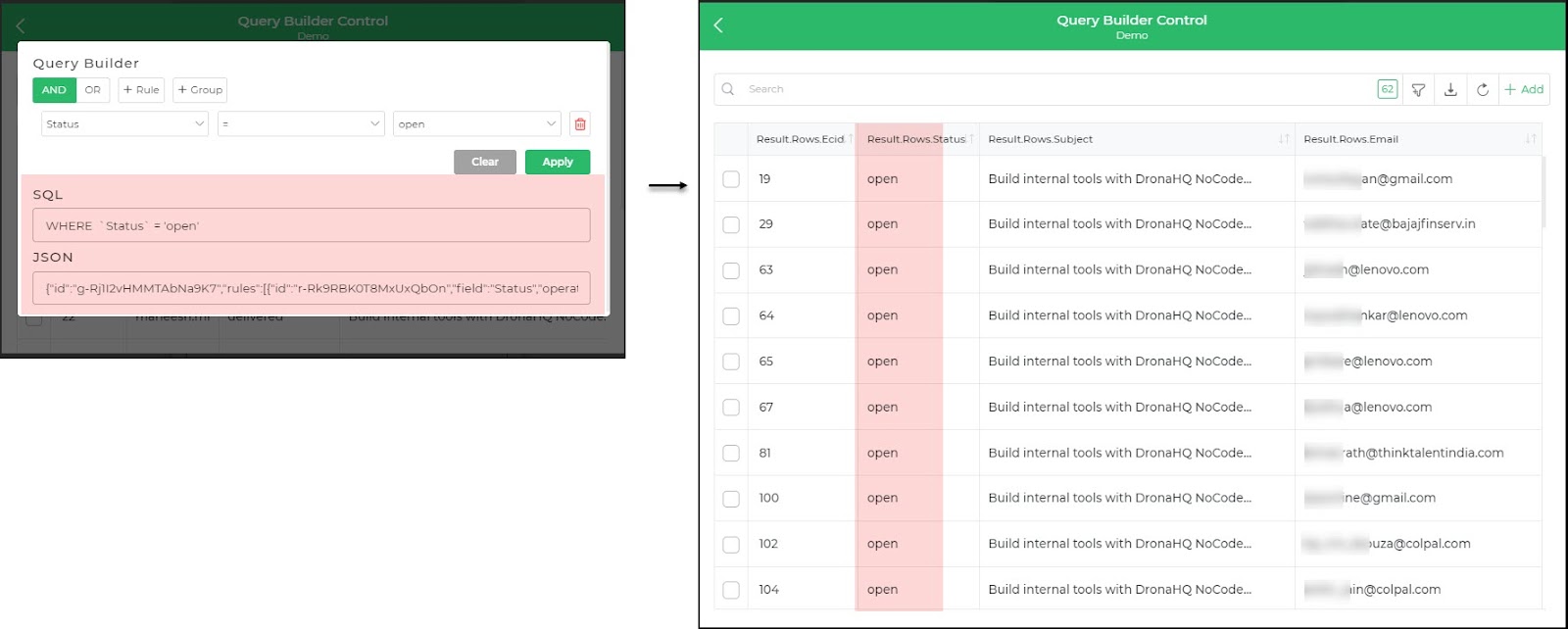
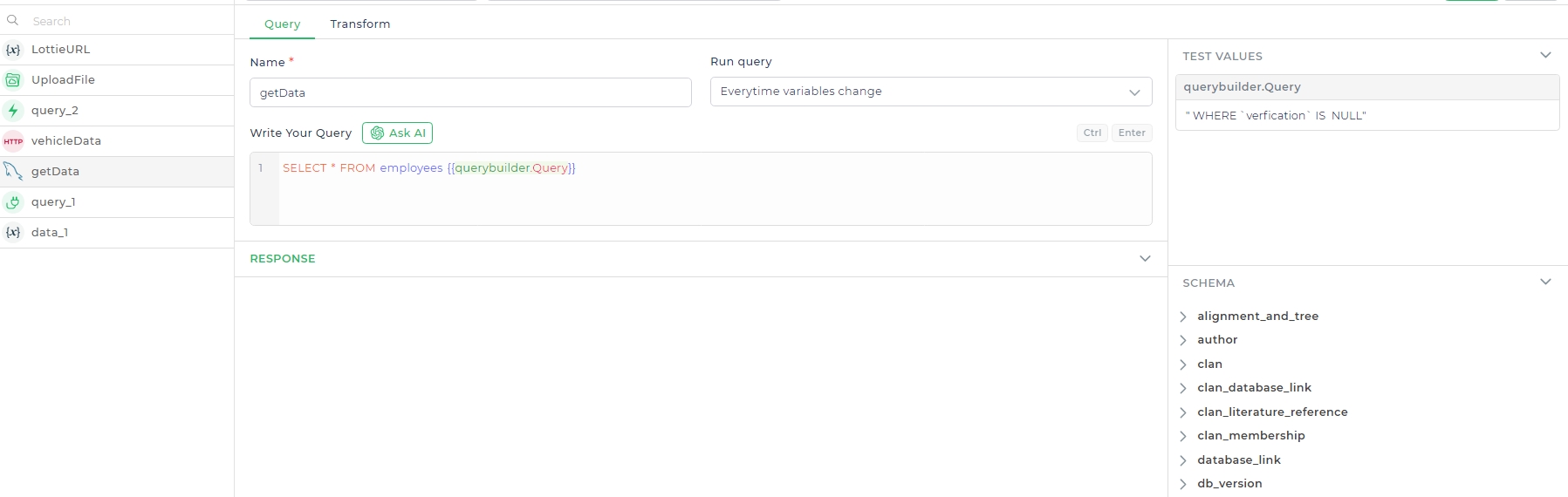
Let's walk through creating a query to fetch data from a MySQL employees table where the verification field is null. This scenario assumes you have a database with an employees table containing fields like id, name, age, department, and verification. The goal is to use a Query Builder to filter out employees who haven't completed verification.
Define Query for MySQL Connector from data:
SELECT * FROM employees {{condition}}In the above, query we are having a variable of
conditionwhich will eventually hold the condition of our Query Builder controlConfigure Control data with the query to passed
WHERE `verfication` IS NULL
Now let's bind the data to a control, whose data we will fetch from the database using our condition query from the control.
- We can bind Data to TableGrid Control:
- While binding, use the
querybuilder.Querykeyword to replace the condition variable in the SQL connector query.
Properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Database | Specifies the type of database (SQL or NoSQL) for sending the query. When using NoSQL, Dynamic Operators can be added. |
| Theme | Defines the color scheme or theme for the composite control. |
| Schema | JSON format containing fields available for use in the query builder. |
| Order By | Toggles the option to include sorting criteria in the query results. |
And here's an example of the Schema for a Product data use case:
[
{
"label": "Product Name",
"value": "ProductName",
"enum": [
{
"label": "Sandwich",
"value": "Sandwich"
},
{
"label": "Burger",
"value": "Burger"
},
{
"label": "All",
"value": ""
}
]
},
{
"label": "Product ID",
"value": "ProductID"
},
{
"label": "Price",
"value": "Price",
"type": "number"
},
{
"label": "Product Quantity",
"value": "Quantity"
},
{
"label":"Product Stock",
"value":"ProductInStock",
"type":"boolean"
},
{
"label":"Created",
"value":"create",
"type":"date",
"date_format": "MM/DD/YYYY",
"submit_format": "UTC"
},
{
"label":"Updated",
"value":"update",
"type":"datetime",
"date_format": "DD/MM/YYYY",
"submit_format": "LOCAL"
},
{
"label":"Delivered",
"value":"DeleiveryTime",
"type":"time",
"date_format": "TIMESTAMP",
"submit_format": "UTC"
}
]
Schema Explanation
The given schema is a structured representation of fields that describe product-related information. Each field in the schema contains a label (the display name) and a value (the key or identifier for the field). Depending on the field's nature, it may include additional metadata like type, date_format, submit_format, and enum options.
Label
- This is the display name for the field.
- It is typically shown to user, to describe what the field it represents.
Value
- This is the unique identifier for the field.
- Unlike the label, this is not typically displayed to end users.
type
- This specifies the data format for the field.
- eg: string, number, boolean, date, datetime, time.
Enum
- The enum key in a schema is used to define a list of predefined, fixed values that a field can accept. It acts as a constraint to restrict the input to only the allowed options.
- Ensures the value for the field is selected from a predefined list.
- Useful for any scenario where the input must be restricted to a specific set of choices.
Note : label and value are required keys, as they define the display name and unique identifier for the field. Whereas type and enum are optional keys
Date Types
There are 3 valid types for date fields:
- date: Only the calendar date without time (e.g., 2024-06-17).
- datetime: Both date and time (e.g., 2024-06-17 14:00).
- time: Only the time in 24-hour format (HH:mm), e.g., 14:30.
- Note: "time" Time fields always follow the 24-hour format (HH:mm).
Date Formats
In date, time, datetime types, we additionally require 2 more keys date_format and submit format. The date_format can only have 4 types:
- ISO: Standard ISO 8601 format, e.g., 2024-06-17T14:00:00Z.
- European: Date in DD/MM/YYYY format.
- US: Date in MM/DD/YYYY format.
- Friendly: Month DD, YYYY User-friendly human-readable formats like "June 17, 2024".
- Timestamp: Represents UNIX timestamp in seconds or milliseconds.
- If the date_format is timestamp, the time will be converted to a UNIX timestamp for submission.
- Note :If no date_format is explicitly provided for a date_format key, it defaults to the ISO standard format YYYY-MM-DD. This ensures consistency and standardization across systems when no specific date format is specified.
Submit Formats
The submit_format determines how date/time data is sent or stored. It has only 2 options.
- UTC: Coordinated Universal Time, independent of the local timezone.
- LOCAL: Time data is submitted in the local system's timezone.
- For UTC format data provided will be considered in UTC TIMEZONE
- Note :If no submit_format is explicitly provided for a submit_format key, it defaults to the LOCAL format.
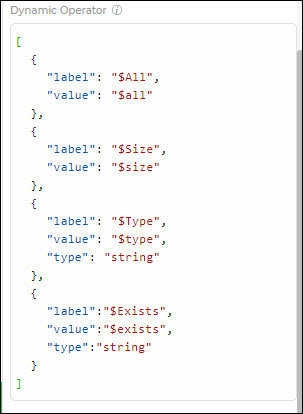
Dynamic Operators
The Dynamic Operators feature in the Query Builder control allows you to add custom operators that are not available by default. This enables you to define specific operators for different types of data you use in your application. You can easily customize the operators to support String type data within DronaHQ.
Key Points:
For String type data, the control automatically adds double quotes to the value field in the resolved output JSON query.
For other data types, you must provide a value that is supported in your NoSQL parameter. For instance, the $all operator expects an array type in the value field, so it's essential to provide an array value in the query control.
To add your specific operators, go to the Dynamic Operator section under Properties, and customize the operators to support String type data in DronaHQ.
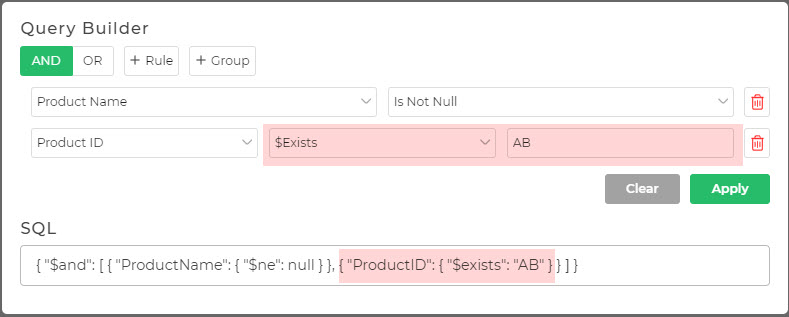
Whenever you run the form and create queries using the additional operators, you will see them listed for String type data. For example, in the illustration provided, the query is built for the Product ID using the $Exists operator.
By leveraging Dynamic Operators, you gain more flexibility and control over your queries, allowing you to tailor them to the specific needs of your application.
Dynamic Operators Example:
Query:
{
"ProductID": {
"$Exists": true
}
}
In this example, the query uses the $Exists operator to check if the Product ID exists in the data.
Control Output
The outputs from the Query Builder control, represented by the placeholders {{querybuilder.Raw_JSON}} and {{querybuilder.Query}}, can be referenced in other controls, data queries, or JavaScript functions using the control's unique name.
| Output | Description |
|---|---|
| querybuilder.Raw_JSON | Represents the query in RAW_JSON format, providing precise control over the query structure. |
| querybuilder.Query | Represents the query in a user-friendly format, simplifying the process of building complex queries. |
Events
| Trigger | Description |
|---|---|
| On_apply | Triggered when you select the query parameters and click the Apply button to apply the specified filters or search criteria. |
| On_clear | Triggered when you click the clear button to reset or remove any applied filters, returning the data to its original state. |